
We all follow diverse life paths, yet a common thread unites our journeys — the unpredictable nature of disability. Disability is more likely than you might assume, as life’s twists teach us. For instance, over 25% of today’s young adults will encounter disability before retirement.
Just like the statistic unveils the unexpected, we delve into the landscape where the odds of needing a safety net are higher than we assume. In today’s ever-unpredictable landscape, understanding short-term and long-term disability options has become indispensable.
This blog aims to navigate these intricate waters, shedding light on the distinctions between short-term vs. long-term disability insurance, enabling you to make an informed decision. So, do you need disability insurance? Let’s find out.
Disability insurance, or disability income insurance, serves as a financial lifeline, protecting your income if unforeseen circumstances disrupt your ability to work. If an unanticipated serious illness or injury disrupts your ability to work, disability insurance replaces a portion of your income.
Like most insurance types, disability insurance offers financial protection in exchange for a monthly fee, known as a premium. Unlike other insurances, you don’t have to meet a minimum spending threshold, or deductible, to get paid. Once medically certified as unable to work, you can receive a portion of your income through disability insurance — typically around 40% to 70% of your salary. This unique flexibility adapts to your situation, ensuring financial security while reflecting a commitment to progress and ongoing learning.
Whether it’s short-term or long-term disability insurance, the coverage extends its wingspan to shield you from various degrees of adversity. Consider it a proactive step, ensuring your financial stability remains unwavering despite life’s uncertainties.
Short-term disability insurance provides income replacement for individuals who cannot work due to a temporary illness, injury or medical condition. Depending on the policy specifics, the insured period can vary from a few weeks to several months.
To help you better understand, consider the following example. Sarah recently had surgery for a non-permanent medical condition. This required her to take four weeks off from work to recover. During these four weeks, she could not go to work — leaving her concerned about her financial responsibilities.
Fortunately, Sarah had short-term disability insurance. This allowed her to file a claim and provide medical documentation confirming her condition. After a short waiting period, her claim was approved. When her short-term disability insurance kicked in, she started to receive a percentage of her pre-disability income as benefits. These benefits helped cover her essential expenses during her recovery.
As a result, Sarah could focus on her health and rehabilitation without the added stress of financial instability. After four weeks of recovery, her doctor cleared her to return to work, and her benefits ceased. Now Sarah’s back at work with peace of mind and financial stability.
From the example above, you can clearly see that short-term disability insurance provides a crucial safety net to working individuals during a temporary health setback.
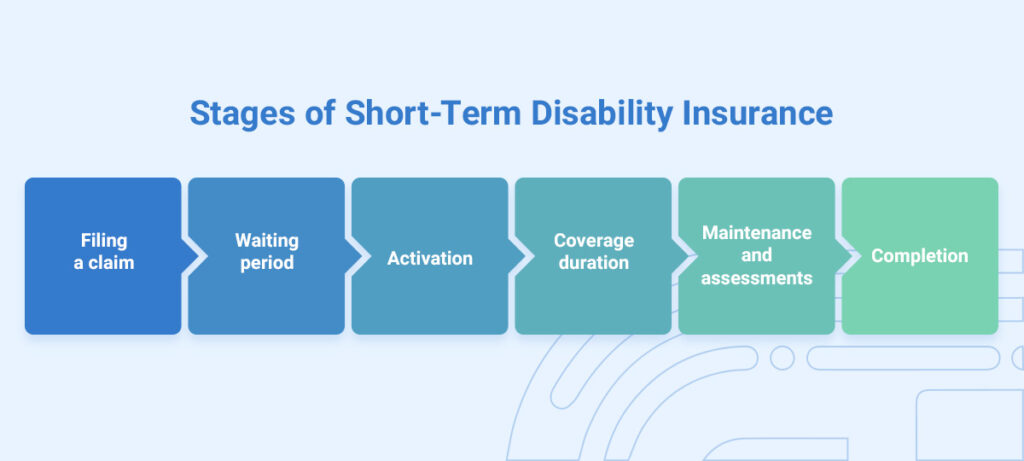
This disability insurance process involves a few key stages, each contributing to the process of securing financial support during a period of incapacity:
Surgery, accidents, pregnancy difficulties, diseases and rehabilitation from various medical treatments are all common medical scenarios covered by short-term disability insurance. The particular situations covered can vary depending on the insurance coverage and the contract terms.
Policyholders receive a percentage of their pre-disability wages throughout the disability term to help them handle critical financial commitments while recovering. Medical bills, rent or mortgage payments, utilities, groceries and other living expenses are typically covered. However, short-term disability insurance may not cover the entire amount of an individual’s pay and may have time limits for coverage.
Exclusions may apply, such as preexisting conditions, injuries received in particular circumstances or elective procedures. This is where the medical documents from a health care provider are required. Understanding the breadth of coverage and making informed decisions about short-term disability insurance requires evaluating policy specifics, waiting periods, benefit percentages and any limitations.
To qualify for short-term disability insurance, you generally must meet the following criteria:
Short-term disability benefits typically start after the completion of a waiting period, which can range from a few days to a few weeks. Once the individual satisfies this waiting period and medical documentation confirms their disability, the benefits will commence payment. The waiting period ensures a specific duration for the disability before it provides benefits and determines how long the policyholder must cover expenses before receiving financial support.
Short-term disability coverage usually lasts for a set time, which can range from a few weeks to a few months, based on the specific policy details. The insurance contract outlines the coverage period and may vary based on factors such as the nature of the disability, the policy terms and the insurance provider. Once the predefined coverage period ends, the policyholder’s short-term disability benefits cease, and they may transition to long-term disability coverage if needed and if they have such a policy in place.

Long-term disability insurance is a form of financial protection that provides ongoing income replacement to individuals who cannot work for an extended period due to a disabling medical condition or injury. Unlike short-term disability insurance, which covers temporary disabilities, long-term disability insurance addresses more prolonged and potentially permanent incapacities that prevent individuals from engaging in substantial gainful employment.
Long-term disability insurance is a crucial safety net that provides financial stability and peace of mind for individuals facing chronic health conditions, severe injuries or disabilities that hinder their capacity to maintain a steady income and meet daily living expenses over the long term.
When a policyholder becomes incapacitated and meets the policy’s definition of disability, they initiate the process by filing a claim with their insurance provider. This often involves submitting comprehensive medical documentation and undergoing evaluations to confirm the disability’s severity and impact on work capacity.
The policyholder becomes eligible for benefits after the elimination period, which can last several months. Once the policyholder satisfies the waiting period and the medical evaluation confirms the disability, the policyholder starts receiving regular benefit payments. These payments usually replace a percentage of the individual’s pre-disability income, often around 50% to 70%, helping to alleviate the economic burden caused by the inability to work.
The duration of benefit payments varies based on the policy’s terms. It can last for a certain number of years or until the policyholder reaches a particular age. To maintain the claim, the insurance company may require regular assessments from medical professionals to verify the ongoing disability.
Long-term disability insurance offers comprehensive financial protection for individuals who experience extended disabilities that hinder their ability to work. This coverage encompasses a wide range of medical conditions, injuries and illnesses that prevent policyholders from engaging in substantial gainful employment.
This type of coverage offers financial support when individuals can no longer perform the essential duties of their current occupation or any occupation for which they are reasonably qualified, depending on the policy terms. Covered conditions may include severe injuries from accidents, chronic illnesses like cancer or heart disease, neurological disorders, musculoskeletal issues and mental health conditions that substantially impair work capacity.
Long-term disability insurance provides benefits that aid policyholders in managing critical expenses during their disability, such as medical bills, housing costs, utilities and day-to-day living necessities.
It’s important to note that policy terms can vary, and some long-term disability insurance policies might have exclusions or limitations for specific conditions, so carefully reviewing the policy details is essential. Long-term disability insurance offers individuals and their families financial security and stability during prolonged periods of incapacity, allowing them to focus on recovery without the added burden of severe income loss.

Long-term disability requirements are typically more stringent than short-term disability insurance. To qualify for long-term disability insurance, you need to meet the following criteria:
Long-term disability benefits typically start after the completion of a waiting period or elimination period. This waiting period can last a few months, during which the policyholder is responsible for covering their expenses. Once the individual satisfies the elimination period and medical evaluation verifies their disability, the long-term disability benefits will begin payment. This waiting period ensures the disability is not temporary before initiating the benefits and determines how long the policyholder must independently manage their finances before receiving ongoing financial support.
Long-term disability coverage can last for an extended period, often ranging from a few years to several decades, depending on the specific policy terms. The duration of coverage is typically outlined in the insurance contract and may depend on factors such as the nature of the disability, the policyholder’s age and the insurance provider. Long-term disability benefits may continue until the policyholder reaches a specified age or until the disability is no longer deemed severe enough to prevent substantial gainful employment.
The decision between short-term and long-term disability insurance depends on your individual circumstances and needs. If you’re concerned about covering immediate expenses during a temporary inability to work, short-term disability insurance could provide crucial financial support for a few weeks to a few months. This can be especially valuable if you lack emergency savings or paid leave.
Conversely, long-term disability insurance offers extended protection for more severe and prolonged disabilities that might last beyond a few months. It ensures financial stability during extended periods of incapacity and can be crucial if you have significant financial responsibilities or lack other long-term income sources.
When applying for life insurance, consider factors such as your current financial situation, savings, family obligations and employer benefits. In some cases, a combination of both types of insurance might be beneficial. It’s important to review policy terms, premiums, waiting periods and coverage limits to make an informed choice that aligns with your unique circumstances and provides the necessary level of protection.
As life presents us with uncertainties, securing the right disability insurance is a proactive step toward ensuring lasting financial stability. The choice between short-term and long-term disability insurance hinges on your unique circumstances. Short-term coverage can offer immediate relief during temporary setbacks, while long-term protection provides a safety net for extended challenges.
We’re your local partner at David Pope Insurance Services, offering tailored solutions safeguarding your well-being. Our experienced team guides you through the intricacies of disability insurance, enabling you to make informed decisions. Remember, the road to resilience involves adaptation — just as we’ve adapted to serve the Midwest’s insurance needs for over two decades.
Contact us online today to craft a personalized disability insurance plan that empowers you to confidently face whatever lies ahead.
